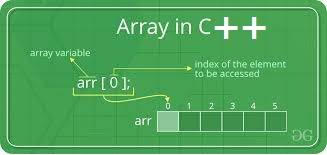
Array C++
We have two types of data structures Linear and Non Linear. Elements in a Linear data structure form a sequence, while elements of nonlinear data structure do not.
Linear data structures are represented in two ways in computer memory. One is called Array and another is called Linked List.
In arrays there is a linear relationship between the elements by means of sequential memory locations.
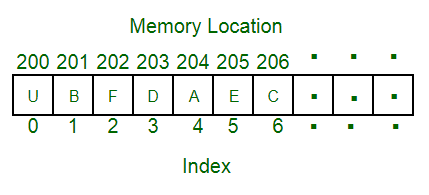
In linked lists the linear relationship between the elements is represented by means of pointers. In linked lists we have nodes and each node contains data elements and a link to another node.
Arrays: An array is a collection finite number of homogeneous data elements described by a single name. so Array is a linear data structure.
By ‘finite’ we mean there are specific number of elements in an array and by ‘homogeneous’ we mean that all elements in an array have same data type.
For example, an integer array contains integer elements only and a character array contains elements of type char only.
An index is used to reference elements in an array. In an ‘n’ element array the index varies from 0 to n-1. i.e the first element in an array has index 0, second element has index 1 and so on.
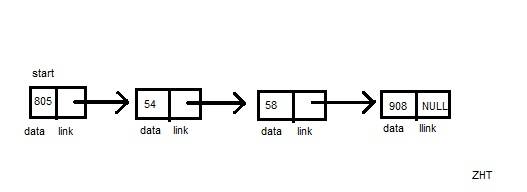
No matter how big an array is, its elements are always stored in contiguous memory locations. In an array each index is associated with a value and each value has a unique address. This is shown below in picture.
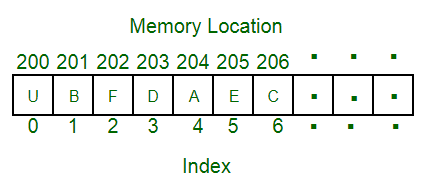 In the picture ‘U’ is element ‘0’ is its index and ‘200’ it its address.
In the picture ‘U’ is element ‘0’ is its index and ‘200’ it its address.
Operations on Arrays:
1. Traversal: Array traversal means processing each element in an array.
2. Search: Finding an element in an array.
3. Insertion: Adding a new element to an array.
4. Deletion: Removing an element from an array.
5. Sorting: Organizing the element in some order.
6. Merging: Combining two arrays into a single array.
7. Reversing: Reversing the elements of an array.
Given below is a C++ program that implements all the array operations mentioned above. Array C++
Note: i am using Dev++ compiler.
Array C++ Program
//Array C++ Data Structures
//techindetail.com
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define max 5
class array
{
int arr[max];
public:
void insert();
void del(int);
void rev();
void display();
void search(int);
void merge();
void sort();
};
void array::insert()
{
cout<<"Enter array elements: "<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<max;i++)
cin>>arr[i];
}
void array::del(int value)
{
int i,j=0;
while(j<max)
{
if (arr[j]==value)
break;
else
j++;
}
if(j==5)
{
cout<<"element not found"<<endl;
return;
}
else
{
int k=j;
for(i=j;i<max-1;i++)
{
arr[i]=arr[i+1];
k++;
}
arr[k]=0;
}
}
void array:: display()
{
cout<<"The array elements are:"<<endl;
cout<<"-------------------------------"<<endl;
for(int j=0;j<max;j++)
cout<<" "<<arr[j]<<endl;
cout<<"-------------------------------"<<endl;
}
void array::rev()
{
for(int i=0;i<max/2;i++)
{
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[max-1-i];
arr[max-1-i]=temp;
}
}
void array::search(int value)
{
int j=0;
while(j<max)
{
if(arr[j]==value)
{
cout<<value<<" is present at index "<<j<<endl;
return;
}
j++;
}
cout<<" value is not found in the list"<<endl;
}
//sorts array in ascending order
void array::sort()
{
int temp;
for(int i=0;i<max;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<max;j++)
{
if(arr[i]>arr[j])
{
temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
}
}
//merges two arrays
int main()
{
array a;
a.insert();
a.display();
cout<<endl;
a.rev();
a.display();
a.del(4);
a.display();
a.search(5);
a.sort();
a.display();
} Code language: C++ (cpp)Related Data Structures
