Linked Lists C++ Introduction
A linked list is a linear type of data structure, which is a sequence of objects or elements which are connected to each other through pointers. It stores the actual data and a link to another node.
The linked list or singly linked list is a data structure or a Node which has two parts data and link.
- Data Part
- Link Part
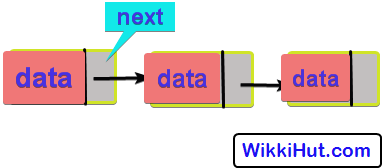
The data part stores the actual data e.g Roll No., Name, etc. And the 2nd part is a pointer to another node, i.e, it stores the address of the next node.
Also Read: Doubly Linked List C++
Linked List C++ Example
Following are the Simple and Easy Steps to Learn actually how we
create and modify linked lists data elements
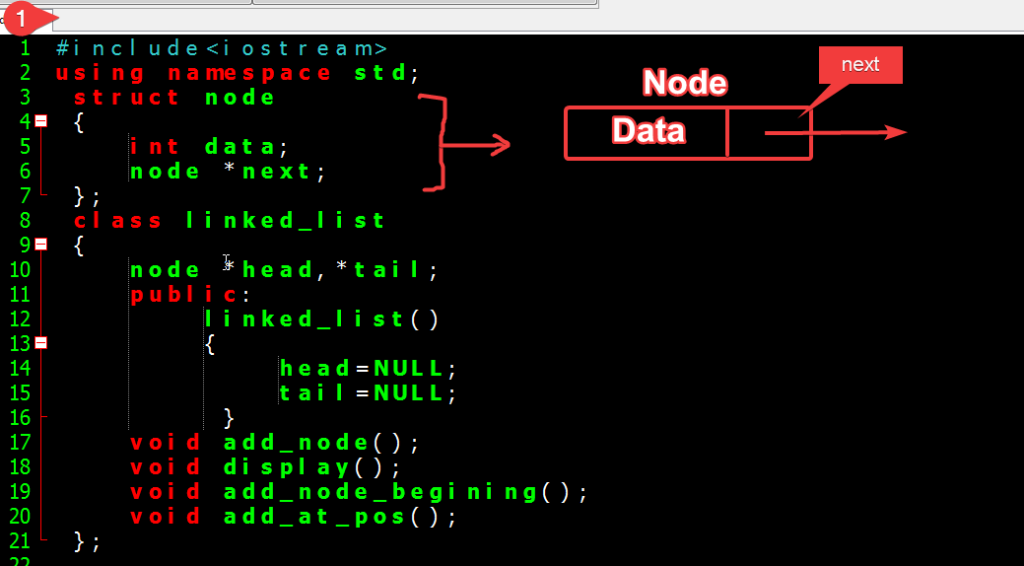
Step 1: Create a structure ( Node ) with two fields.
- Liike int data which stores the actual data elements.
- Node *Next is a pointer that holds the memory address of another node.
- Now just make a class where we call functions like adding or displaying elements of a linked list.
See Also: Stack using Linked List C++
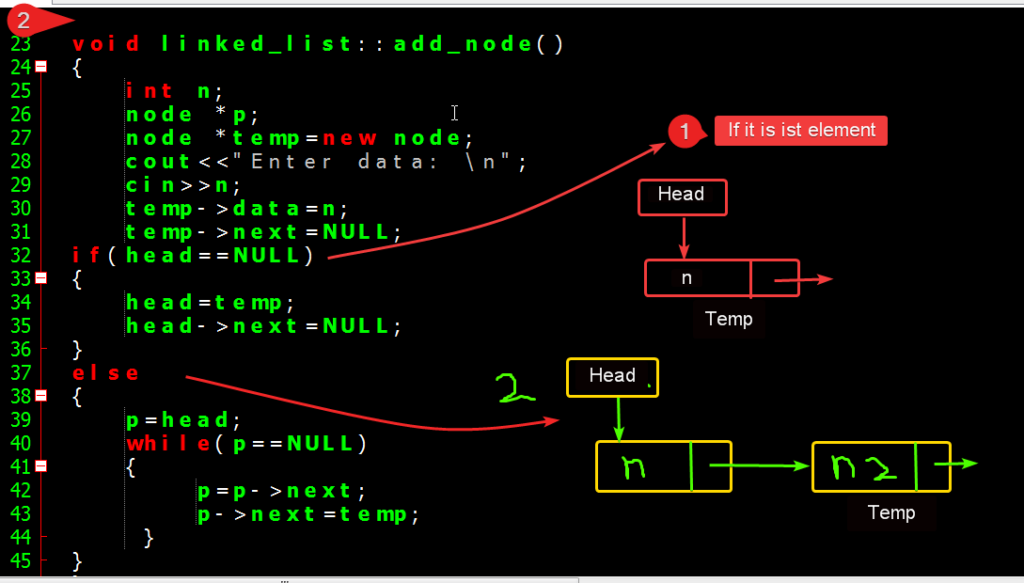
Step 2. Insertion in linked list Nodes.
Define a function which adds data to the Node.
Step 3: Display Data
Suggestion: Doubly Circular Linked List C++
Linked Lists C++ Program
//Linked List C++ Program
//techindetail.com
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node *next;
};
class linked_list
{
node *head;
public:
linked_list()
{
head=NULL;
}
void add_node();
void display();
void add_node_begining();
void add_at_pos();
};
void linked_list::add_node()
{
int n;
node *p;
node *temp=new node;
cout<<"Enter data: \n";
cin>>n;
temp->data=n;
temp->next=NULL;
if(head==NULL)
{
head=temp;
head->next=NULL;
}
else
{
p=head;
while(p->next!=NULL)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->next=temp;
}
}
//function to display elements
void linked_list::display()
{
node *temp;
temp=head;
cout<<"values in linked list are:\n";
cout<<endl;
while(temp!=NULL)
{
cout<<" "<<temp->data<<" -->";
temp=temp->next;
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
void linked_list::add_node_begining()
{
int n;
node *p;
node *temp=new node;
cout<<"enter value: ";
cin>>n;
temp->data=n;
temp->next=NULL;
if(head==NULL)
{
head=temp;
head->next=NULL;
}
else
{
p=head;
temp->next=p;
head=temp;
}
}
void linked_list::add_at_pos()
{
int n, i, pos, counter=0;
node *temp=new node;
node *p,*ptr;
cout<<"enter postion at which to insert: ";
cin>>pos;
cout<<"enter value: ";
cin>>n;
temp->data=n;
temp->next=NULL;
p=head;
while(p!=NULL)
{
p=p->next;
counter ++;
}
if(pos==1)
{
if(head==NULL)
{
head=temp;
head->next=NULL;
}
else
{
ptr=head;
head=temp;
head->next=ptr;
}
}else if(pos>1 || pos<=counter)
{
p=head;
for(i=1; i<pos; i++)
{
ptr=p;
p=p->next;
}
ptr->next=temp;
temp->next=p;
}else
cout<<"position out of order: \n";
}
int main()
{
linked_list object;
while(1){
cout<<"enter 1 for add: 2 for display:3 for add-begining";
cout<<" 4 for add-pos: 5 for exit: \n";
int ch;
cin>>ch;
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
object.add_node();
break;
case 2:
object.display();
break;
case 3:
object.add_node_begining();
break;
case 4:
object.add_at_pos();
break;
case 5:
return 0;
default:
cout<<"wrong choice:\n";
}
}
return 0;
//techindetail.com
}Code language: C++ (cpp)Suggested: Circular Linked List C++
Difference between Linked List and Array
Linked List or Singly Linked list is a linear data structure like Arrays. But in Arrays, the data is stored in contiguous locations and the size is fixed.
But in linked lists, the data is stored at different locations and is linked or connected through Pointers thus making it a dynamic data structure that grows and shrinks at the run time with our needs.
Also Read: Binary Search Tree
Types Of Linked Lists
- Singly-linked list
- Doubly linked list
- Circular linked list
- Doubly Circular Linked List
Singly Linked List
When we say linked list, we are talking about a singly linked list. It has only two parts i.e, the data part and a link part
Doubly Linked List
Every node in the doubly linked list has three fields that are Left_Pointer, Right_Pointer, and Data. It stores the data as well as links to the next and previous nodes.
Circular Linked List
It is just like a singly linked list, except the last node in the list stores the address of the first node of the list instead of the NULL value.
Doubly Circular Linked List
A doubly circular linked list is a double linked list in which the last node stores the address of the first node, and the first node stores the address of the last node.
Some Related Articles
- Doubly Linked Lists
- Stack using Arrays
- Queue Using Arrays
- Circular Linked List
- Tree Data structure
- Graph Data structure
